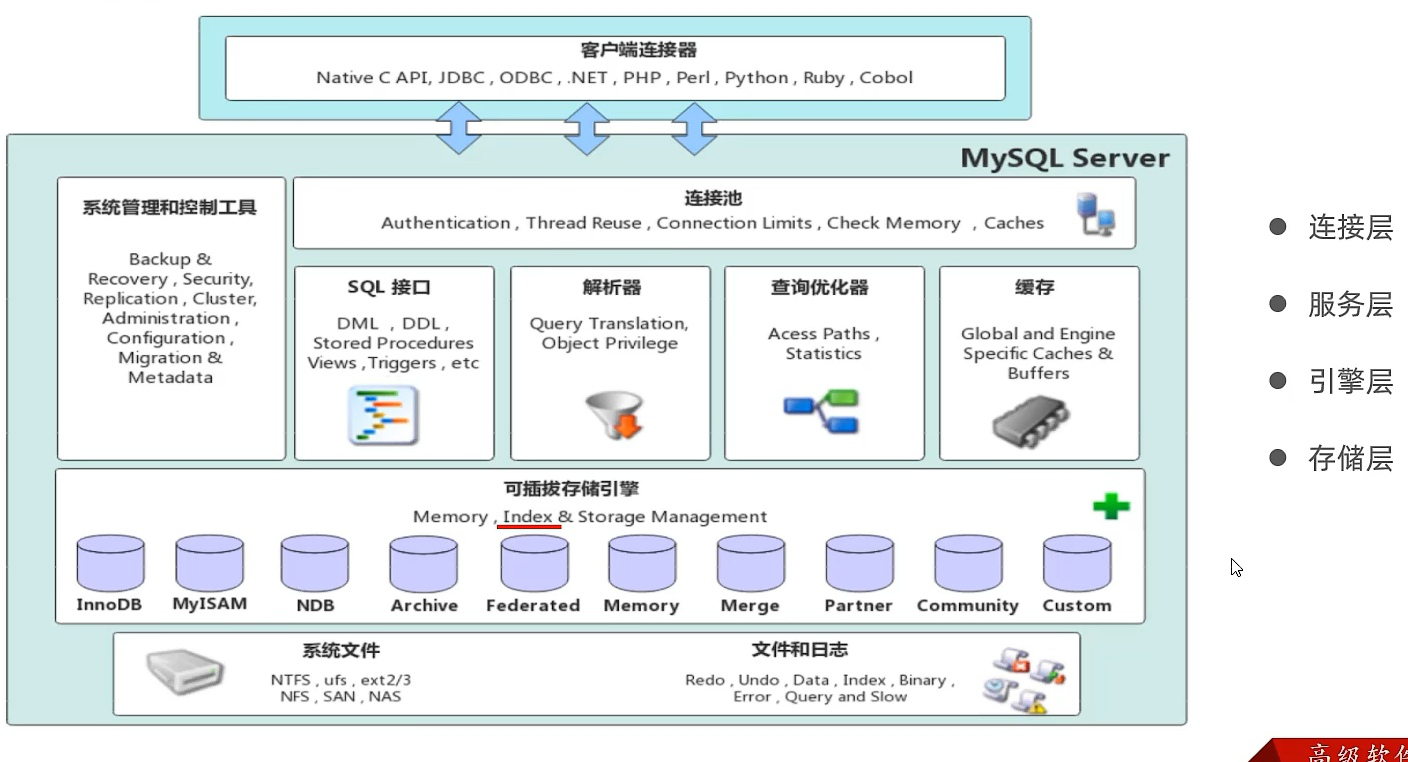
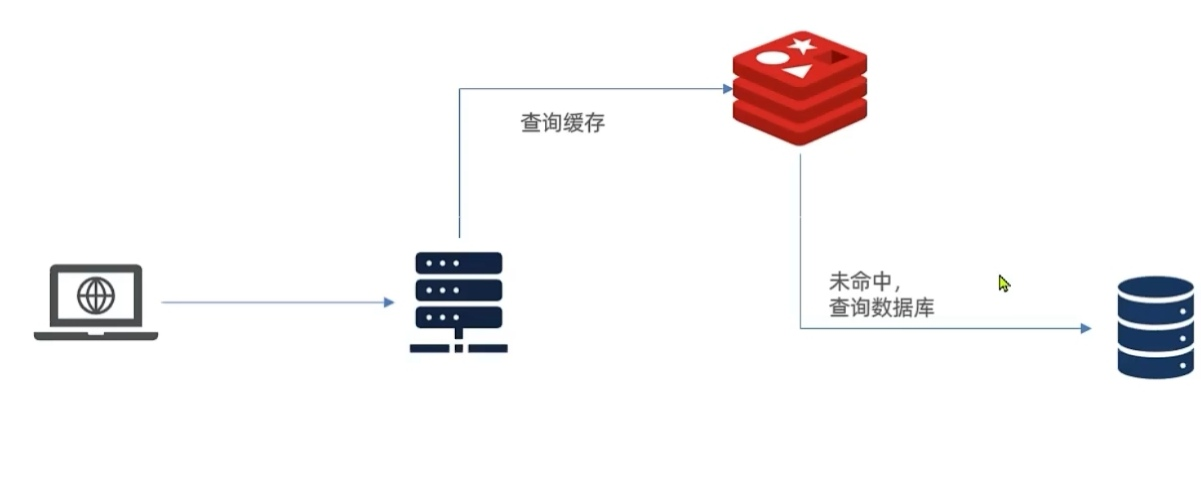
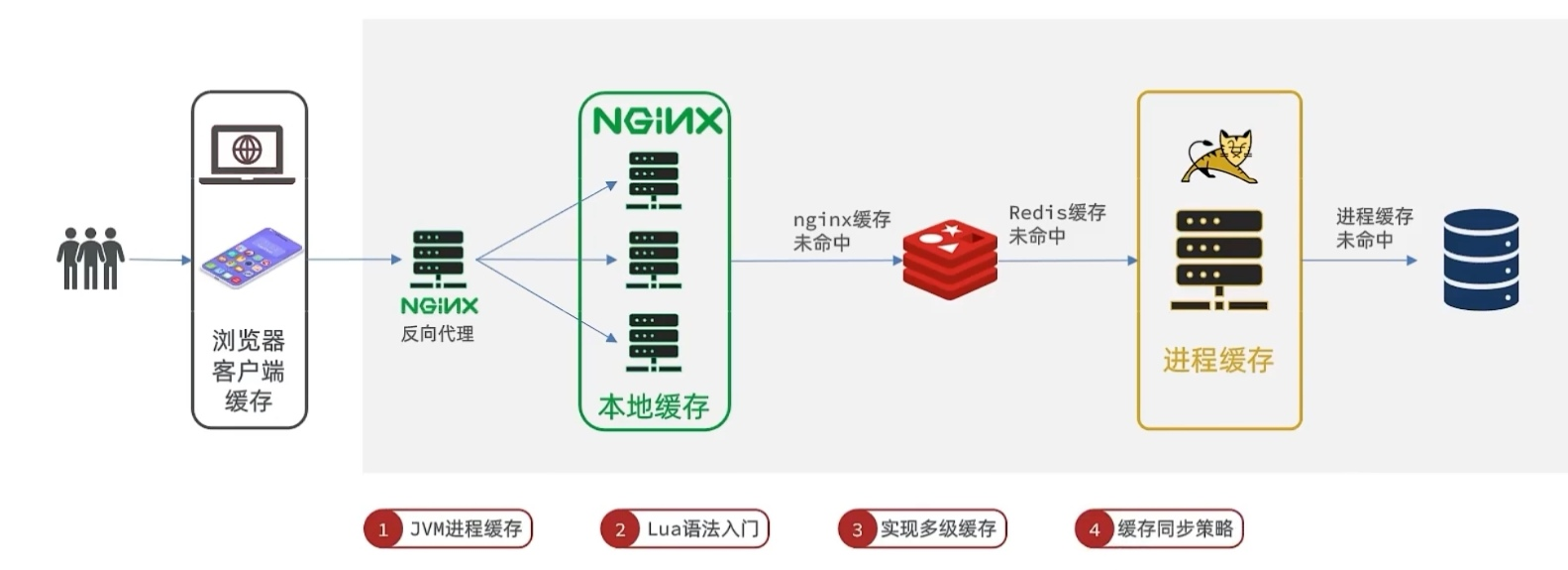
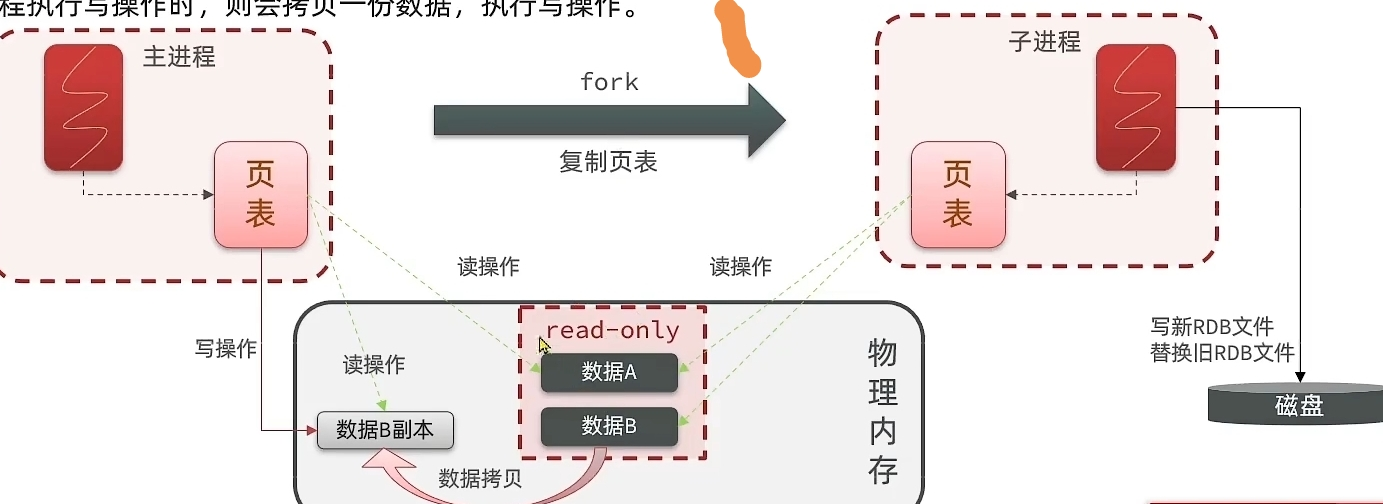
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
std::thread timer_thread([&]()
{
while (true) {
static unsigned int s_seq = 0;
int size = sizeof(SStunLogin) + g_strDeviceId.size() - 1;
char* buf = new char[size];
SStunLogin* p = (SStunLogin*)buf;
p->head.len = htons(size);
p->head.cmd = htons(STUN_CMD_LOGIN);
p->head.seq = htonl(++s_seq);
p->nat = g_finalNatType;
memcpy_s(p->uid, size - sizeof(SStunLogin) + 1, g_strDeviceId.c_str(), g_strDeviceId.size());
sendto(sockfd, buf, size, 0, (const sockaddr*)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
delete[] buf;
printf("udp stun alive seq = %u\n", s_seq);
sleep(30);
} });
int epoll_fd = epoll_create(1);
if (epoll_fd < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Failed to create epoll" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
struct epoll_event event;
event.events = EPOLLIN;
event.data.fd = sockfd;
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, sockfd, &event) < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Failed to add socket to epoll" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
const int MAX_EVENTS = 10;
struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENTS];
while (true)
{
int num_events = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
if (num_events < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Error in epoll_wait" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_events; ++i)
{
if (events[i].data.fd == sockfd && events[i].events & EPOLLIN)
{
char buf[1500];
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
ssize_t num_bytes = recvfrom(sockfd, &buf, sizeof(buf), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &addr_len);
if (num_bytes < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Error in recvfrom" << std::endl;
continue;
}
printf("recvfrom %s_%d size = %ld\n", inet_ntoa(client_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port), num_bytes);
if (sizeof(SStunLoginResponse) == num_bytes)
{
SStunLoginResponse *slr = (SStunLoginResponse *)buf;
if (ntohs(slr->head.cmd) == STUN_CMD_LOGIN && ntohs(slr->head.len) == num_bytes)
{
printf("recv stun alive result = %d,seq = %u,ip = %s,port = %d\n", (int)slr->result, ntohl(slr->head.seq),
IpInt2Str(slr->ip).c_str(), ntohs(slr->port));
}
}
if (sizeof(SStunTransfer) == num_bytes)
{
SStunTransfer *st = (SStunTransfer *)buf;
if (ntohs(st->head.cmd) == STUN_CMD_TRANSFER && ntohs(st->head.len) == num_bytes)
{
SStunResponse response;
response.head.cmd = st->head.cmd;
response.head.seq = st->head.seq;
response.head.len = htons(sizeof(response));
response.result = 0;
int tmpRet = sendto(sockfd, (const char *)&response, sizeof(response), 0, (sockaddr *)&client_addr, addr_len);
if (tmpRet != sizeof(response))
{
printf("sendto %s_%d ret = %d,error = %d\n", IpInt2Str(client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr).c_str(), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port), tmpRet,
errno);
}
client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = st->ip;
client_addr.sin_port = st->port;
tmpRet = sendto(sockfd, "0", 1, 0, (sockaddr *)&client_addr, addr_len);
if (tmpRet != 1)
{
printf("sendto %s_%d ret = %d,error = %d\n", IpInt2Str(client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr).c_str(), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port), tmpRet,
errno);
}
printf("stun to %s_%d\n", IpInt2Str(client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr).c_str(), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port));
}
}
else
{
std::cout << "receive data " << string(buf, num_bytes) << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
|